Community Land Model Urban Meets Reinforcement Learning
Investigating the Efficacy and Impacts of RL-Based HVAC Control on Indoor and Local Urban Climates.
Junjie Yu, John S. Schreck, David John Gagne, Keith W. Oleson, et al.


Core Highlights
- Integrated Model: First integration of RL-based HVAC control strategies within an urban climate model.
- Balance: Effectively balances energy use reduction with thermal comfort maintenance.
- Variability: Impact on local urban climate varies significantly across different cities.
- Generalization: Models trained in climate-diverse cities show better transferability.
Abstract
AI-Driven Urban Adaptation
Reinforcement learning (RL)-based HVAC control offers an innovative path for urban climate adaptation. However, its interaction with background climate remains complex. This study proposes an integrated framework combining RL with the Community Land Model Urban (CLMU) to evaluate efficacy, impacts, and transferability.
Our findings reveal that "rewards" (balancing energy & comfort) are highly sensitive to background climate. Cities in hot climates achieve higher rewards, while cities with high temperature variability produce more transferable RL policies. This suggests that city-to-city learning could be a viable strategy for deploying smart HVAC controls globally.
Key Insight
Transferability & Climate Variability
The study found a strong correlation between seasonal temperature variation and RL policy transferability.
Cities with larger seasonal temperature swings act as better "training grounds." RL agents trained in these environments learn robust strategies that adapt well to other locations, unlike agents trained in stable climates.
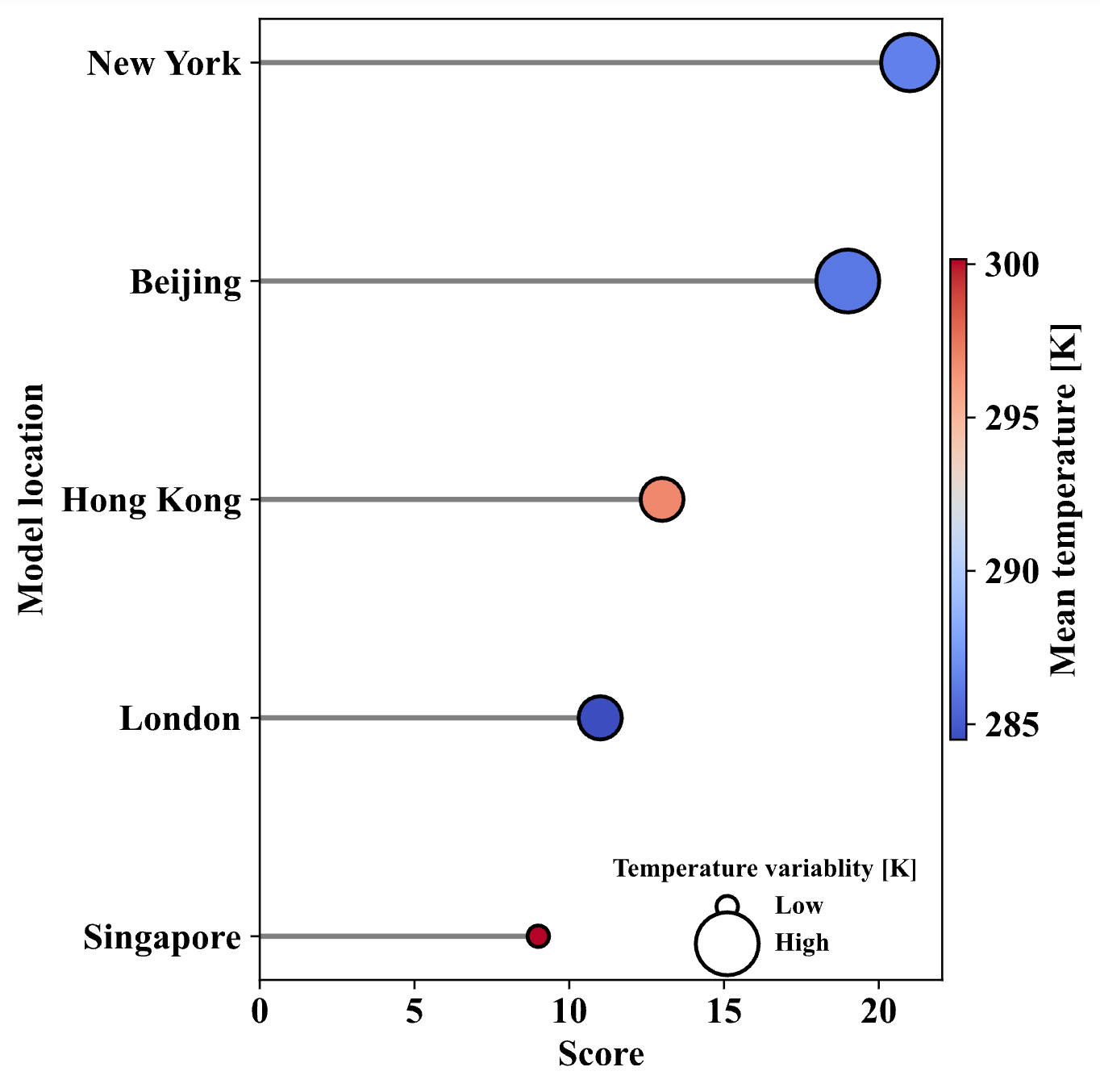
Figure: Transferability score vs Temperature Variability
Presentation
Research Slides
Comprehensive overview of the RL framework, experimental setup, and cross-city analysis.